Science Note
[Apr. 30, 2024] Previous Science Note
Inducible and Inhibitory Organelles in Neurodegeneration
|
In neurodegeneration, dysfunctional mitochondria contribute to oxidative stress and energy deficits in neurons. Lysosomes, responsible for the disposal of cellular waste, may be impaired, leading to the accumulation of damaged organelles, including mitochondria. At the same time, abnormal lipid metabolism and accumulation of lipid droplets have been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, potentially exacerbating neuronal dysfunction and contributing to disease progression. The intricate relationships between dysfunctional mitochondria, impaired lysosomal function and abnormal lipid metabolism underscore the complex pathophysiology of neurodegeneration. |
|||||||||||
|
Messenger RNA transport on lysosomal vesicles maintains axonal mitochondrial homeostasis and prevents axonal degeneration |
APOE4/4 is linked to damaging lipid droplets in Alzheimer’s disease microglia |
Loss of WIPI4 in neurodegeneration causes autophagy-independent ferroptosis |
|||||||||
|
Point of Interest - Lysosome–kinesin adaptor related complex (BORC) KO depletes axonal mRNAs mainly encoding ribosomal and mitochondrial/oxidative phosphorylation proteins. - This depletion leads to mitochondrial defects and ultimately to axonal degeneration in neurons. - A mechanistic connection of BORC deficiency may accelerate common neurodegenerative disorders. |
Point of Interest - Lipid droplet-associated enzyme ACSL1-positive microglia was most abundant in patients with AD having the APOE4/4 genotype. - In microglia, fibrillar Aβ induces ACSL1 expression, triglyceride synthesis and lipid droplet accumulation depending on APOE. - Conditioned media from lipid droplet-containing microglia lead to Tau phosphorylation and neurotoxicity depending on APOE in neurons. |
Point of Interest - WIPI4 deficiency causes β-Propeller protein-associated neurodegeneration, which induces ferroptosis via an autophagy-independent mechanism in cell culture and in zebrafish. - WIPI4 depletion increases the localization of ATG2A at ER-mitochondrial contact sites, which enhances phosphatidylserine import into mitochondria. - This leads to increased mitochondrial synthesis of phosphatidylethanolamine, a major lipid prone to peroxidation and ultimately to ferroptosis. |
|||||||||
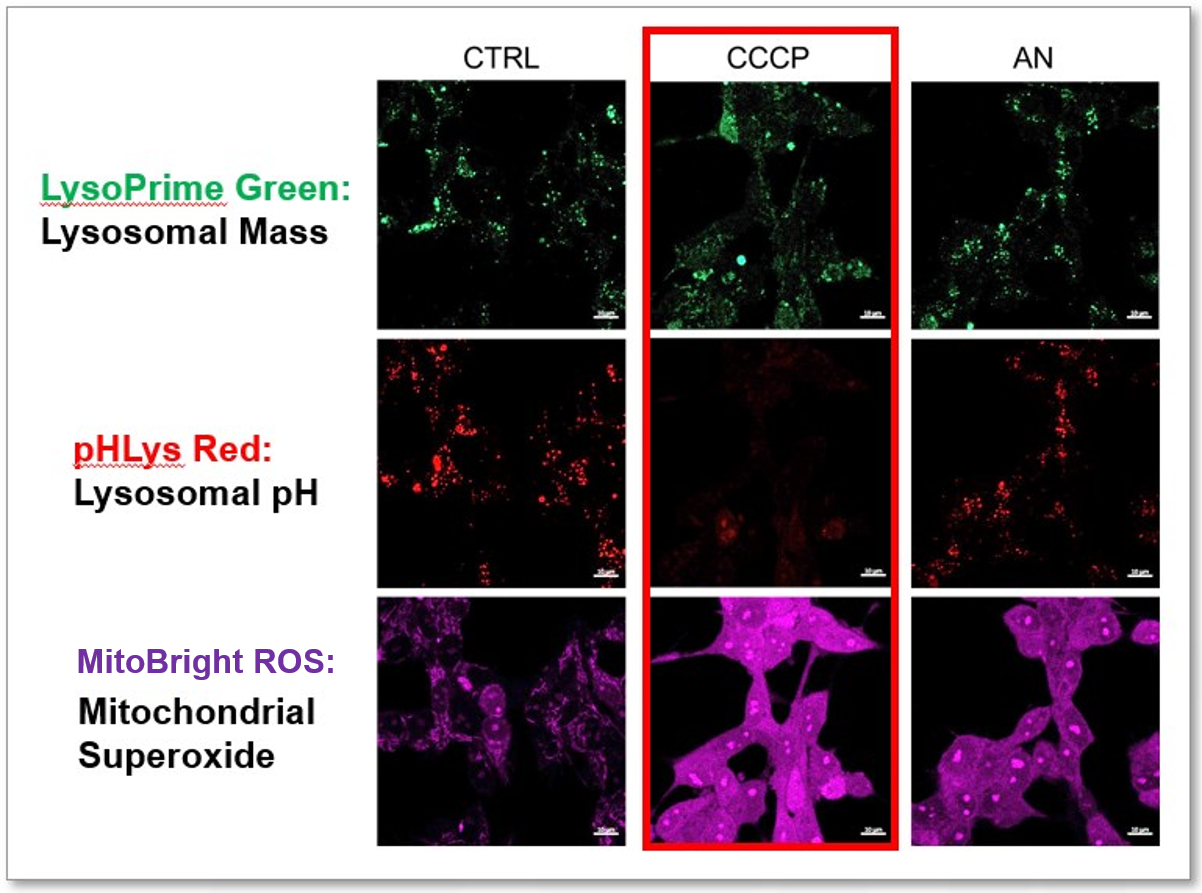
| Related Techniques | |||||||||||
| Mitochondrial or internal lipid peroxide detection | MitoPeDPP, Liperfluo | ||||||||||
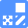
| Mitochondrial or internal iron detection | Mito-FerroGreen, FerroOrange | ||||||||||
| Mitophagy or autophagy detection | Mitophagy Detection Kit, Autophagic Flux Assay Kit | ||||||||||
| Glycolysis/Oxidative phosphorylation Assay | Extracellular OCR Plate Assay Kit, Glycolysis/OXPHOS Assay Kit | ||||||||||
| Lipid droplets detection | Lipi-Blue/Green/Red/Deep Red | ||||||||||
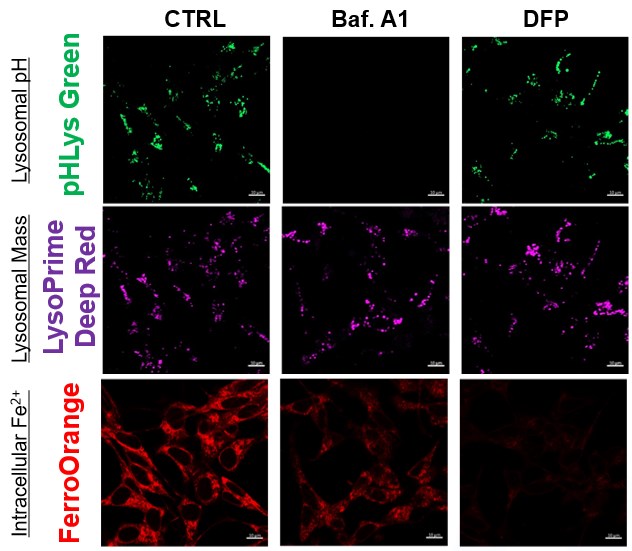
| Lysosome staining | pH-dependent (pHLys Red) and pH resistance (LysoPrime Green/Deep Red) probes | ||||||||||
| Lysosomal acidic pH detection |
Lysosoml Acidic pH Detection Kit-Green/Red and Green/Deep Red |
||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||
| Related Applications | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||