-Bacstain- CTC Rapid Staining Kit (for Flow cytometry)
Bacterial Staining
- Highly sensitive fluorescence detection
- No washing required
-
Product codeBS01 -Bacstain- CTC Rapid Staining Kit (for Flow cytometry)
| Unit size | Price | FUJIFILM Wako Products code |
|---|---|---|
| 100 assays | ¥25,700 | 348-91301 |
| 100 assays | ・CTC ・Enhancing reagent A |
10 mg x3 100 μlx1 |
|---|
Description
Colony formation using an agar plate is a very common and reliable method for counting bacterial cells. However, it takes quite a long time to form a colony. Therefore, alternative detection methods have been developed. Bacteria-specific gene amplification methods such as PCR, LAMP, and nucleus staining are quite rapid, but these methods count dead bacteria as well. Therefore, detection of live cell functions is essential to determining the actual number of living bacteria in a sample. Tetrazolium salts can be used to detect respiratory activity of bacterial cells or mitochondria. CTC is a tetrazolium salt and is reduced by this respiratory activity to form fluorescent CTC formazan on the cell surface. Therefore, CTC is used for specific staining of aerobic live bacteria and can be applied to hard-to-culture bacteria (VNC: viable but non-culturable). CTC forms a fluorescent formazan by an electron transfer system. However, CTC alone is not sensitive enough to stain single cells. Therefore, the CTC-Rapid Staining Kit contains an enhancing reagent that improves the CTC staining efficiency. Compared with staining with CTC only, this staining kit enables rapid and sensitive staining of microorganisms. Maximum wavelengths of the CTC formazan dye are 430 nm or 480 nm for excitation and 630 nm for emission.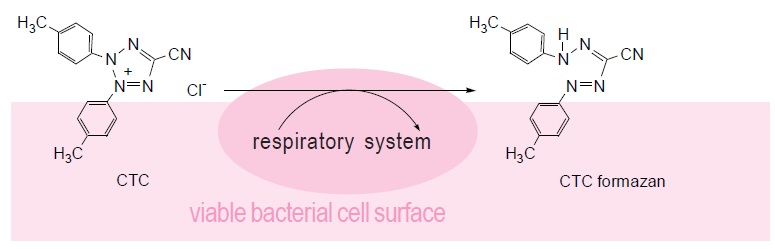 Fig. 1 Bacterial cell viability detection mechanism with CTC
Fig. 1 Bacterial cell viability detection mechanism with CTC
Manual
Technical info
Microscopy detection
1. Centrifuge bacteria culture and remove the supernatant, and then resuspend the bacteria pellet with PBS(-).
2. Add CTC + Enhancing reagent-B. Incubate at 37°C for 1 hour.
3. Prepare a slide and detect fluorescence by B-excitation filter set.
Flow cytometry detection
1. Centrifuge bacteria culture and remove the supernatant, and then resuspend the bacteria pellet with PBS(-).
2. Add CTC + Enhancing reagent-A. Incubate at 37°C for 1 hour.
3. Analyze the cells with a flow cytometry: 488 nm excitation, 630 nm emission.
FACS Data
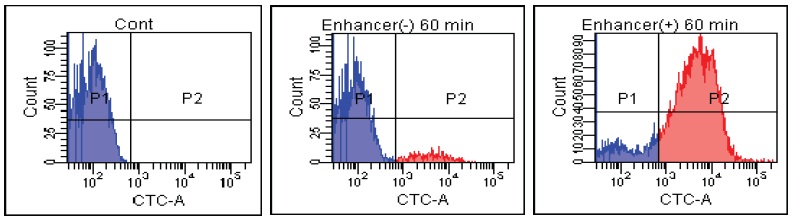
E. coli
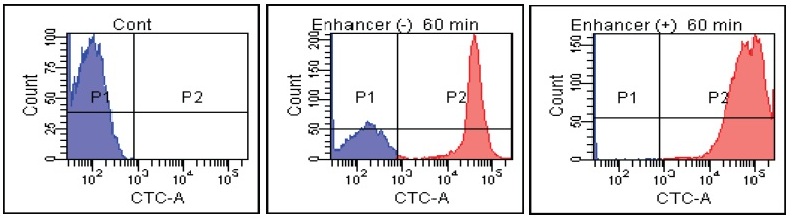
B. Subtilis
Candida albicans
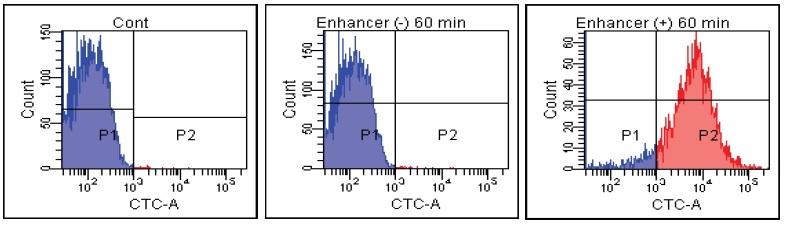
E. faecalis
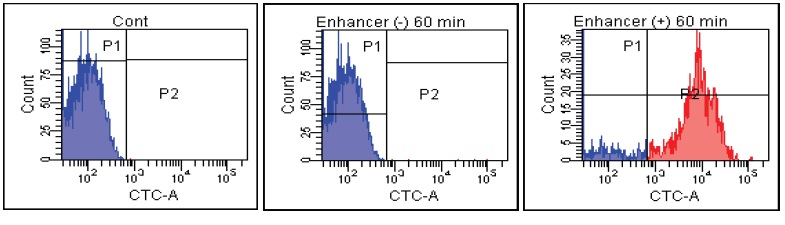
Fig. 2 CTC staining of various microorganisms with and without Enhancing reagent.
Experimental Example
Observation by Microscopy
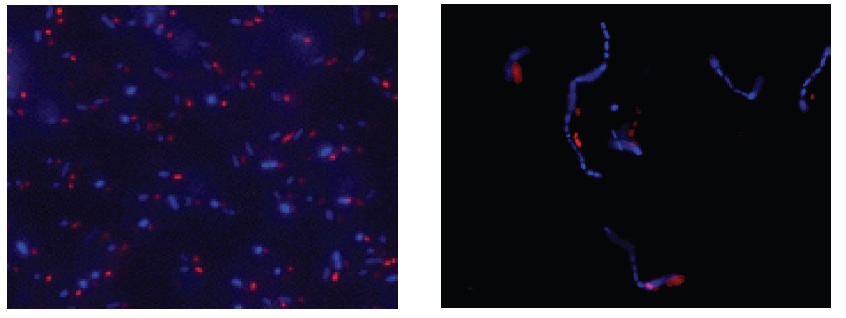
Fig. 3 E. coli staining (left) and L. casei staining (right) with CTC and DAPI. Bacterial cells were stained with CTC Rapid Staining Kit first, and then 1 μl of DAPI solution was added. The cells were incubated at room temperature for 5 min. Formaldehyde fixation with 1-4% formaldehyde can be performed before DAPI staining.
References
1) A. W. Coleman, "Enhanced Detection of Bacteria in Natural Environments by Fluorochrome Staining of DNA", Limnol. Oceanogr., 1980, 25, 948.
2) E. Severin, J. Stellmach and H. -M. Nachtigal, "Fluorimetric Assay of Redox Activity in Cells", Anal. Chim. Acta, 1985, 170, 341.
3) G. G. Rodriguez, D. Phipps, K. Ishiguro and H. F. Ridgway, "Use of a Fluorescent Redox Probe for Direct Visualization of Actively Respiring Bacteria", Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1992, 58(6), 1801.
4) G. Schaule, H. C. Flemming and H. F. Ridgway, "Use of 5-Cyano-2,3-ditolyl Tetrazolium Chloride for Quantifying Planktonic and Sessile Respiring Bacteria in Drinking Water", Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1993, 59(11), 3850.
5) R. A. Bovill, J. A. Shalloross and B. M. Markey, "Comparison of the Fluorescent Redox Dye 5-Cyano-2,3-ditolyltetrazolium Chloride with p-Iodonitrotetrazolium Violet to Detect Metabolic Activity in Heat-stressed Listeria monocytogenes Cells", J. Appl. Bacteriol., 1994, 77(4), 353.
6) M. T. E. Suller and D. Lloyd, "Flow Cytometric Assesment of the Postantibiotic Effect of Methicillin on Staphylococcus aureus", Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1998, 42(5), 1195.
7) M. Kawai, N. Yamaguchi and M. Nasu "Rapid Enumeration of Physiologically Active Bacteria in Purified Water Used in the Pharmaceutical Manufacuturing Process", J. Appl. Microbiol., 1999, 86, 496.
8) N. Yamaguchi, M. Sasada, M. Yamanaka and M. Nasu, "Rapid Detection of Respiring Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Apple Juice, Milk and Ground Beef by Flow Cytometry", Cytometry , 2003, 54A, 27.
9) A. Kitaguchi, N. Yamagauchi and M. Nasu, "Enumeration of Respiring Pseudomonas spp. in Milk within 6 Hours by Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Following Formazan Reduction", Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2005, 71(5), 2748.
10)A. Hiraishi and N. Yoshida, "An Improved Redox Dye-Staining Method Using 5-Cyano-2,3-Ditoryl Tetrazolium Chloride for Detection of Metabolically Active Bacteria in Activated Sludge", Microbes Environ., 2004, 19(1), 61.
Handling and storage condition
| 0-5°C, Protect from light | |
|
Danger / harmful symbol mark |

|
|---|---|