-Cellstain- Hoechst 33342 solution

Nucleus Dye
-
Product codeH342 -Cellstain- Hoechst 33342 solution
-
CAS No.23491-52-3(Hoechst 33342:free base)
-
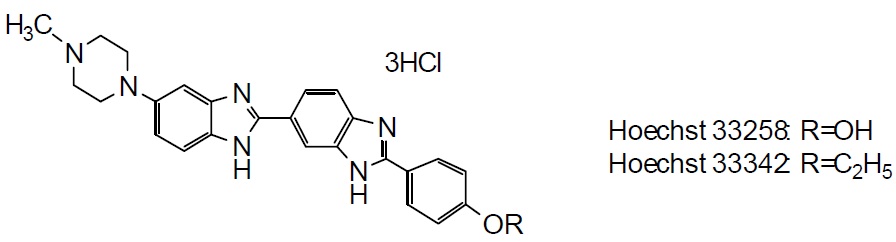
Chemical name2'-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-5-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2,5'-bi-1H-benzimidazole, trihydrOchloride, solution
-
MWC27H31Cl3N6O=561.93
| Unit size | Price | FUJIFILM Wako Products code |
|---|---|---|
| 1 ml | ¥5,700 | 346-07951 |
Product Description
Hoechst dyes are cell membrane permeable and stain DNA to emit intense blue fluorescence. They bind to DNA in the minor groove of poly-AT sequence rich areas. Both Hoechst 33342 and Hoechst 33258 are water-soluble and stable in aqueous solutions. The excitation and emission wavelengths of Hoechst-DNA complex are 350 nm and 460 nm, respectively.
Chemical Structure
Technical info
Staining Procedure
1.Prepare 10-50 μM Hoechst dye solution with PBS or an appropriate buffer.a)
2.Add Hoechst dye solution with 1/10 of the volume of cell culture medium to the cell culture.b)
3.Incubate the cell at 37ºC for 10-20 min.
4.Wash cells twice with PBS or an appropriate buffer.
5.Observe the cells under a fluorescence microscope with 350 nm excitation and 460 nm emission filters.
a) Since Hoechst dyes may be carcinogenic, extreme care is necessary during handling.
b) Or you may replace the culture medium with 1/10 concentration of Hoechst dye buffer solution.
Staining Data
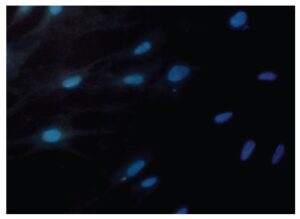
Fig. 2 Cell staining with Hoechst 33258
Cell type: human fetal cell
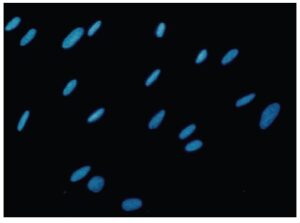
Fig. 3 Cell staining with Hoechst 33342
Cell type: human fetal cell
References
1. M. J. Lydon, et al., Vital DNA Staining and Cell Sorting by Flow Microfluorometry. J Cell Physiol. 1980;102:175-181.
2. M. Sriram, et al., Structural Consequences of a Carcinogenic Alkylation Lesion on DNA: Effect of O6-ethylguanine on the Molecular Structure of the d(CGC[e6G]AATTCGCG)-netropsin Complex. Biochemistry. 1992;31:11823-11834.
3. Y. Tadokoro, et al., Characterization of Histone H2A.X Expression in Testis and Specific Labeling of Germ Cells at the Commitment Stage of Meiosis with Histone H2A.X Promoter-Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein Transgene. Biol Reprod. 2003;69:1325-1329.
4. F. Wada, et al., Analyses of Expression and Localization of Two Mammalian-Type Transglutaminases in Physarum polycephalum, an Acellular Slime Mold. J Biochem. 2004;136:665-672.
5. T. Ohara, et al., FoSTUA, Encoding a Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein, Differentially Regulates Development of Three Kinds of Asexual Spores, Macroconidia, Microconidia, and Chlamydospores, in the Fungal Plant Pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Eukaryot Cell. 2004;3:1412-1422.
Handling and storage condition
| Appearance: | Yellow liquid |
|---|---|
| Dye content: | To pass test |
| 0-5°C, Protect from light |