Science Note: Lysosome
Lysosomal pH regulated by LAMP proteins [July 11, 2023]
Open / Close the Article
|
Through a combination of various scientific methods, this research reveals the vital role of human lysosome-associated membrane proteins (LAMP-1 and LAMP-2) in maintaining lysosomal pH balance. Despite being mainly recognized as lysosomal markers, LAMP-1 and LAMP-2 directly influence the lysosomal cation channel TMEM175, aiding the acidification of lysosomes to a pH level that optimizes hydrolase activity. Interruptions to the interaction between LAMP and TMEM175 can increase lysosomal pH, impairing their hydrolytic function. |
|
|
Lysosomal LAMP proteins regulate lysosomal pH by direct inhibition of the TMEM175 channel Point of Interest |
|
| Related Techniques | |
| Lipid droplets detection | Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit-Green/Red, Green/Deep Red |
| Lysosome staining | pH-dependent (Red) and pH-independent (Green / Deep Red) probes |
| Autophagy detection | DAPGreen / DAPRed (Autophagosome detection), DALGreen (Autolysosome detection) |
| Endocytosis detection | ECGreen |
| Endocytic internalization assay | AcidSensor Labeling Kit |
| Plasma membrane staining | PlasMem Bright Green / Red |
| Total ROS detection | Highly sensitive DCFH-DA or Photo-oxidation Resistant DCFH-DA |
| Related Applications | |
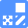
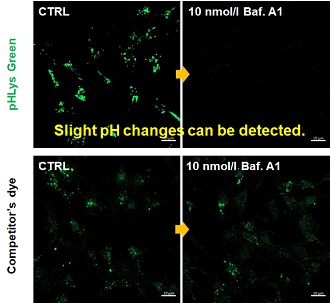
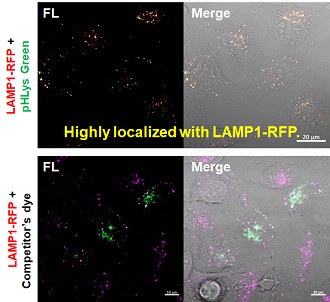
Accurate Measurement for Lysosomal pH changesExisting lysosomal pH detection reagents have issues with dye localization, pH sensitivity, and retention. pHLys Green is a dye that solves these issues. The improved dye retention and localization enable detection of normal lysosomes, and the improved pH sensitivity enables detection of slight pH changes.
Product in Use: Related Product: |
|
Link Lysosomal Failure to Ferroptosis in Human Neurons [May 9, 2023]
Open / Close the Article
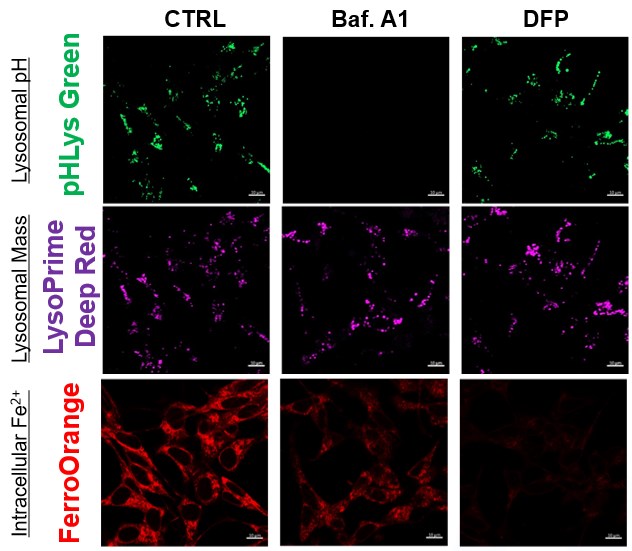
| Here, the scientists reveal an unexpected role for the lysosomal protein prosaposin (PSAP), the knockdown of which caused the formation of lipofuscin, a hallmark of aging, which traps iron, generating reactive oxygen species and triggering ferroptosis. Intriguingly, PSAP deficiency caused these dramatic phenotypes only in neurons, but not in other cells. Learn how the authors used Dojindo's Ferroptosis-related products, FerroOrange and Liperfluo for detecting Iron levels and lipid peroxidation, in their study. | |||||
|
Genome-wide CRISPRi/a screens in human neurons link lysosomal failure to ferroptosis Ruilin Tian, et. al., Nature Neuroscience (2022) Point of Interest |
|||||
| Related Techniques | |||||
| Intracellular lipid peroxidation measurement | Liperfluo | ||||
| Mitochondria lipid peroxidation measurement | MitoPeDPP | ||||
| Intracellular ferrous ion (Fe2+) detection | FerroOrange | ||||
| Mitochondria ferrous ion (Fe2+) detection | Mito-FerroGreen | ||||
| Mitochondrial superoxide detection | MitoBright ROS Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection | ||||
| Lysosomal function assay | Lysosomal pH and mass detection Kit | ||||
| Cellular senescence detection (Live cell imaging or FCM) | Cellular Senescence Detection Kit | ||||
| Cellular senescence detection (Plate reader) | Cellular Senescence Plate Assay Kit | ||||
| Related Applications | |||||
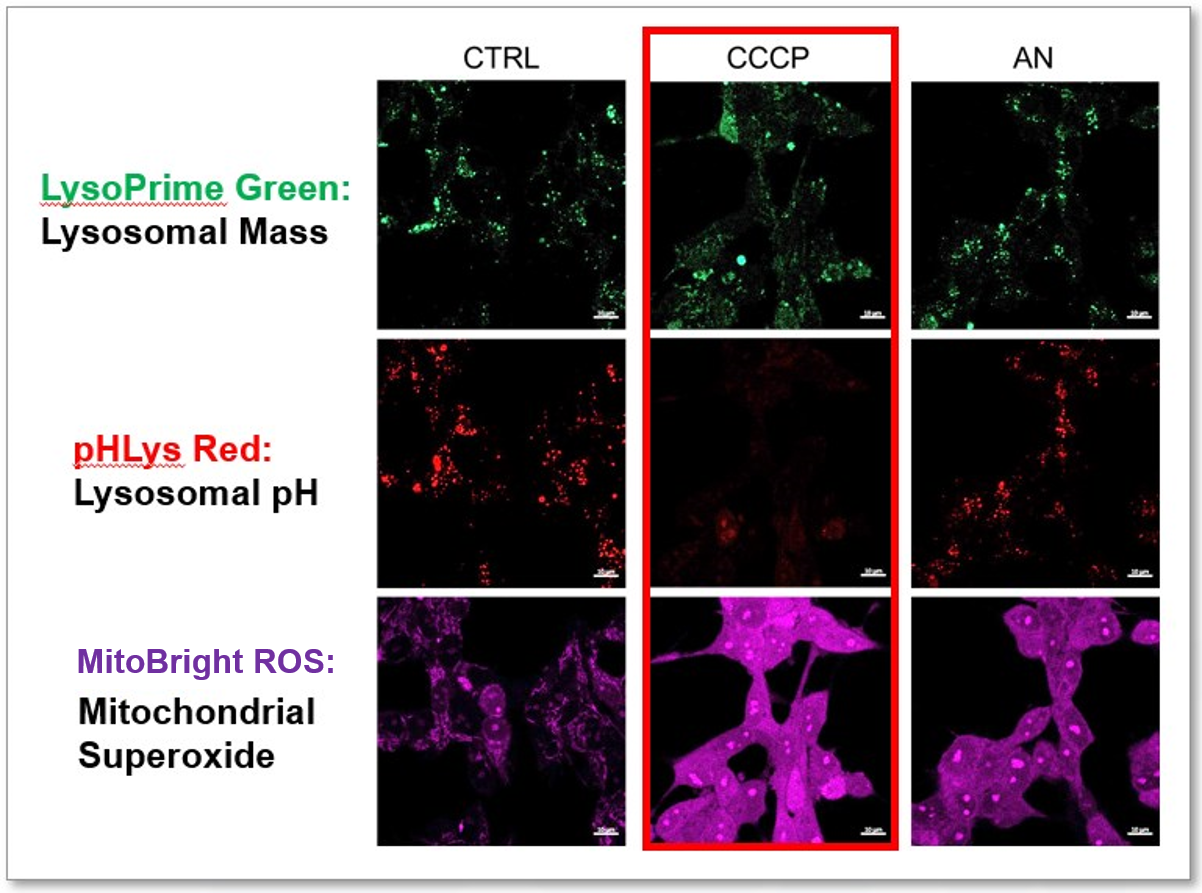
The simultaneous detection of lysosomal function with Mitochondrial ROS and intracellular Fe2+
|
|||||
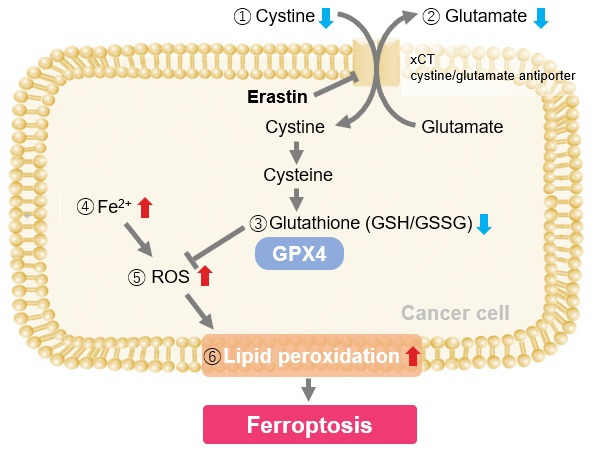
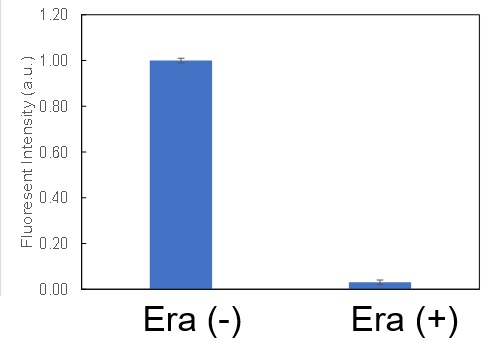
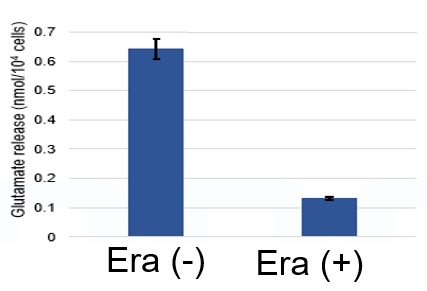
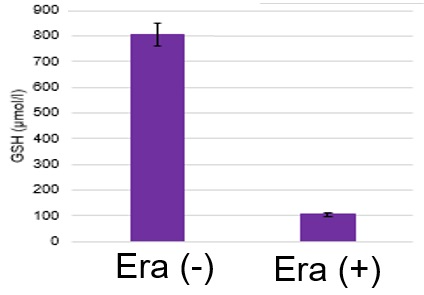
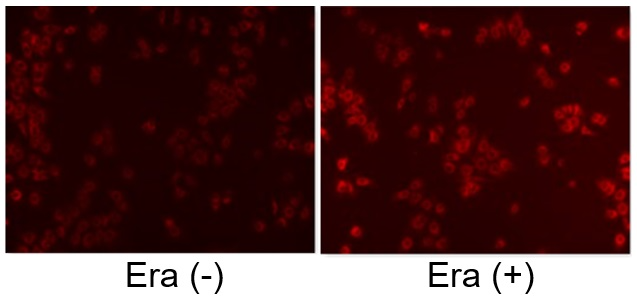
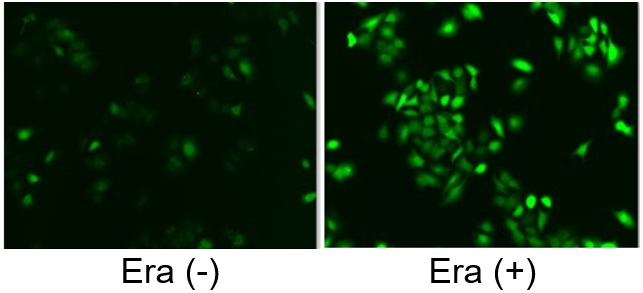
Induction of Ferroptosis by ErastinErastin is a known inducer of ferroptosis. By inhibiting the cystine transporter (xCT), erastin inhibits the uptake of cystine. Cystine is the raw material for GSH. Therefore, Erastin ultimately decreases the amount of GSH. Decreased GSH then results in lipid peroxide accumulation and induction of ferroptosis. Using erastin-treated A549 cells, we measured intracellular Fe2+, ROS, lipid peroxide, glutathione, glutamate release into the extracellular space, and cystine uptake. As a result, inhibition of xCT by elastin was observed and also the release of glutamate and uptake of cystine were decreased. Furthermore, elastin treatment decreased intracellular glutathione while it increased intracellular Fe2+ , ROS, and lipid peroxides.
|
|||||
Various Functional Pathways in Lysosomes [Feb. 7, 2023]
Open / Close the Article
| Lysosomes play a critical role in cellular metabolism and waste management. They are essential for maintaining cellular health and preventing the buildup of cellular waste, which can lead to disease and dysfunction. Understanding the functions of lysosomes is critical for developing treatments for a variety of diseases and disorders. Today, we introduce you to three highlighted articles focusing on lysosomal exocytosis, lysosomal AMPK pathway, and lysosomal pH optimization. | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lysosomal exocytosis in synucleinopathy models | Metformin and lysosomal AMPK pathway | Lysosomal pH optimum and Parkinson's disease |
| Lysosomal exocytosis releases pathogenic α-synuclein species from neurons in synucleinopathy models (Ying Xue Xie, et al., Nature Communications, 13, 4918, 2022) |
Low-dose metformin targets the lysosomal AMPK pathway through PEN2 (Teng Ma, et al., Nature, 603, 159-165, 2022) |
Parkinson’s disease-risk protein TMEM175 is a proton-activated proton channel in lysosomes (Meiqin Hu, et al., Cell, 185, 2292-2308, 2022) |
|
|
|
| Related Technique in This Topic | ||
| Lysosomal function assay | Lysosomal pH and mass detection Kit HOT | |
| Lysosome staining | pH-dependent (Red) and pH-independent (Green / Deep Red) probes HOT | |
| Autophagy detection | DAPGreen / DAPRed (Autophagosome detection), DALGreen (Autolysosome detection) | |
| Endocytosis detection | ECGreen | |
| Endocytic internalization assay | AcidSensor Labeling Kit HOT | |
| Extracellular vesicles labeling | ExoSparkler Exosome Membrane Labeling Kit-Green, Red, Deep Red | |
| Extracellular vesicles Isolation | ExoIsolator Exosome Isolation Kit HOT | |
| Total ROS detection | High Sensitive DCFH-DA HOT or Compatible with Immunostaining HOT | |
Learn more about application data with multiple products here