|
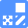
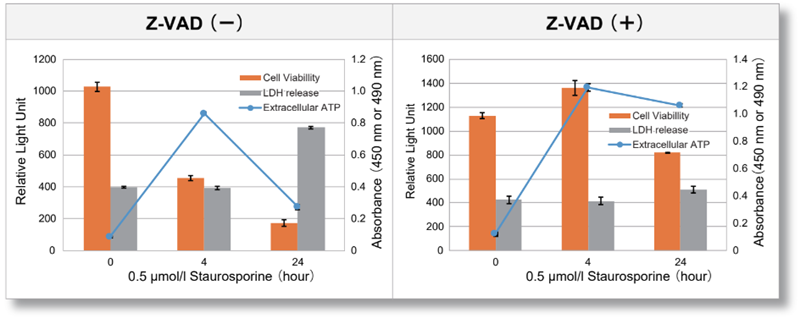
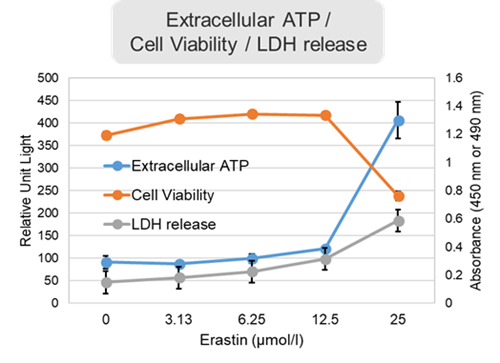
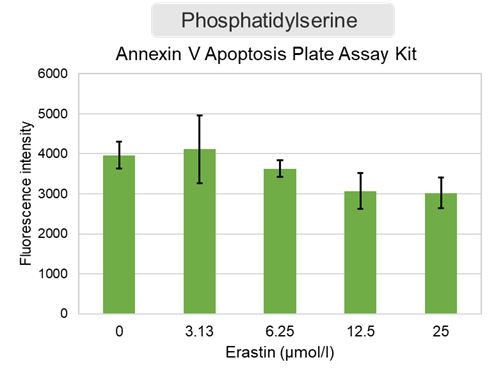
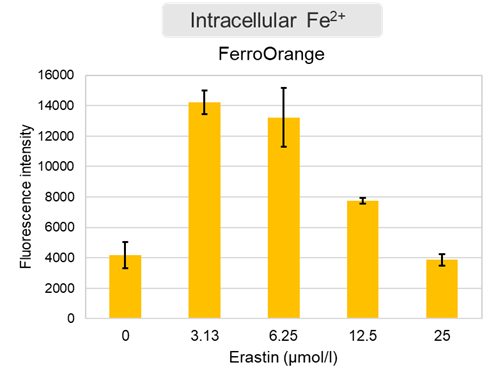
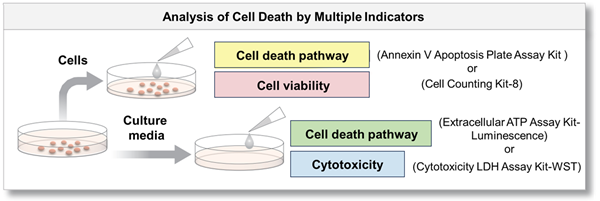
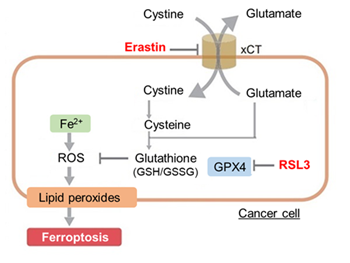
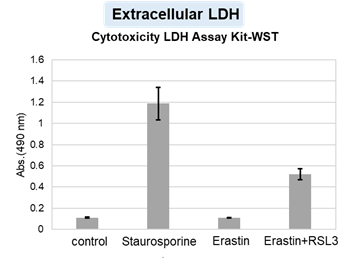
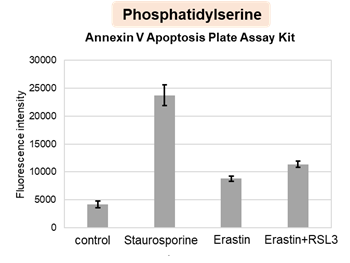
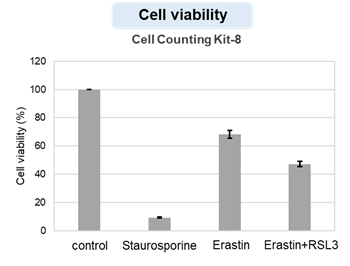
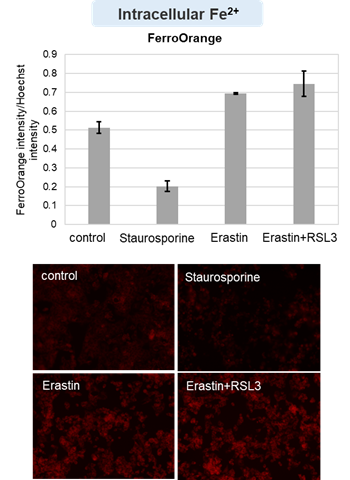
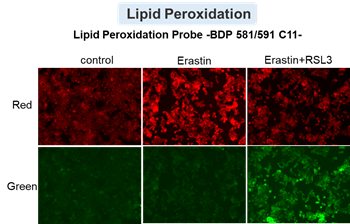
Changes in extracellular ATP release, cell viability, extracellular LDH release, phosphatidylserine, and intracellular Fe2+ were evaluated in HeLa cells treated with various concentrations of Erastin, a ferroptosis inducer, for 24 hours. The results showed that cell viability decreased and extracellular ATP release and extracellular LDH increased in cells treated with Erastin concentration of 25 μmol/l, indicating that cell death was induced under high concentration conditions. Interestingly, the increase in extracellular ATP in the early phase of stimulation, which was observed with the apoptosis inducer Staurosporine, was not observed with Erastin (See Experimental Example: Evaluation using Staurosporine-treated Cells.). Although the apoptosis-related marker phosphatidylserine was not significantly altered by Erastin treatment at any concentration. The amount of intracellular Fe2+, a ferroptosis-related marker, was significantly increased under the low-concentration treatment condition, indicating that it tends to increase before actual cell death occurs.
|
<Product in use>
Extracellular ATP:
Extracellular ATP Assay Kit-Luminescence
Extracellular LDH:
Cytotoxicity LDH Assay Kit-WST
Cell viability: Cell Counting Kit-8
Phosphatidylserine:
Annexin V Apoptosis Plate Assay Kit
Intracellular Fe2+: FerroOrange
|