Science Note
Senescence at the Heart of Cancer and Neurodegeneration [Jun. 17, 2025]
| Cellular senescence is recognized as an important contributor to cancer development through its effects on the tumor microenvironment, and also to age-related dysfunction in both the peripheral and central nervous systems. This ScienceNote introduces recent findings that highlight the tumor-promoting role of senescent fibroblasts in breast cancer, the contribution of senescent neurons to age-associated pain, and the accumulation of senescent neurons through abnormal cell cycle activity in neurodegenerative conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||
|
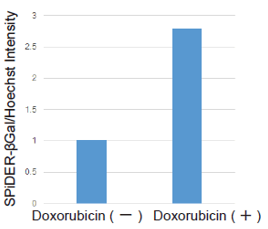
Senescent CAFs mediate immunosuppression and drive breast cancer progression (Cancer Discov., 2025) Highlighted technique: To examine how senescent CAF-derived ECM affects NK cell function, doxorubicin-treated mouse mammary fibroblasts were cultured for six days to deposit ECM in vitro. After cell removal, the ECM was used in NK cytotoxicity assays, with NK cells pre-incubated on the matrix before co-culture with labeled target cells. Related technique SA-βGal Detection(Cell) |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Aging and injury drive neuronal senescence in the dorsal root ganglia (Nature Neuroscience, 2025) Highlighted technique: This study assessed DRG neuron senescence using multiple markers. Aging-related senescence was confirmed by increased SA-β-gal activity, and injury-induced senescence was evaluated by examining the upregulation of p16, p21, and SASP factors including IL-6. Related technique SA-βGal Detection(Tissue) |
||||||||||||||||||
|
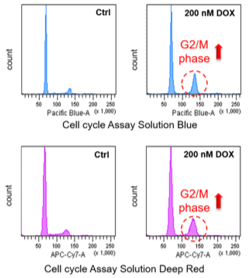
Neuronal cell cycle reentry events in the aging brain are more prevalent in neurodegeneration and lead to cellular senescence (PLoS Biol., 2024) Highlighted technique: To identify rare neurons that start dividing again, the researchers analyzed RNA data from individual cell nuclei collected from multiple human brain samples. They used a list of 350 genes related to the cell cycle and a scoring method to find excitatory neurons that are normally non-dividing but showed signs of abnormal cell cycle activity. Related technique Cell Cycle Assay |
||||||||||||||||||
Related Techniques (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||
Application Note I (click to open/close)
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
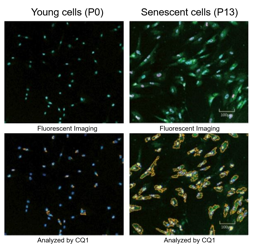
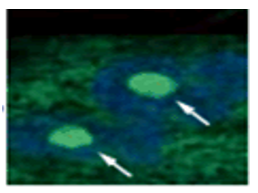
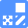
The senescent cell detection dye SPiDER Blue (SG07) and the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) dye MT-1 (MT13) were used to stain human microglial cells. Microscopy revealed that, compared to control cells, senescence-induced cells showed reduced MMP and increased SPiDER Blue fluorescence, reflecting elevated SA-β-Gal activity. *This data was kindly provided by Dr. Supriya D. Mahajan, Department of Medicine, Jacobs School of Medicine & Biomedical Sciences. 1. Seed human microglia cells into a dish and incubate in an incubator set at 37 ℃ and equilibrated with 95% air and 5% CO2. |
Application Note II (click to open/close)
> Increased Senescence in Aged Adipose Tissue
|
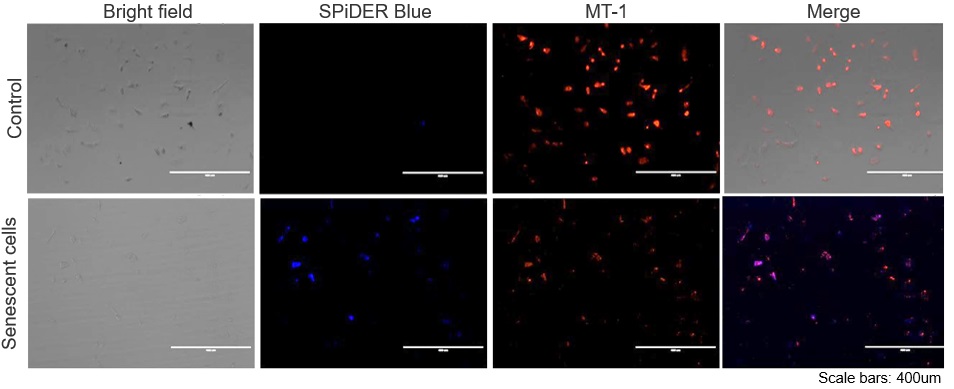
Frozen liver adipose tissue sections from 8-week-old and 35-week-old mice were stained with senescence detection probes SPiDER Blue (SG07) and SPiDER-βGal (SG02). Confocal microscopy revealed a marked increase in fluorescence intensity only in the 35-week-old samples, indicating an age-associated accumulation of senescent cells in older tissue. 1. 8-week-old and 35-week-old mouse liver adipose tissue (frozen sections) samples were prepared on glass slides. [Detection conditions] |




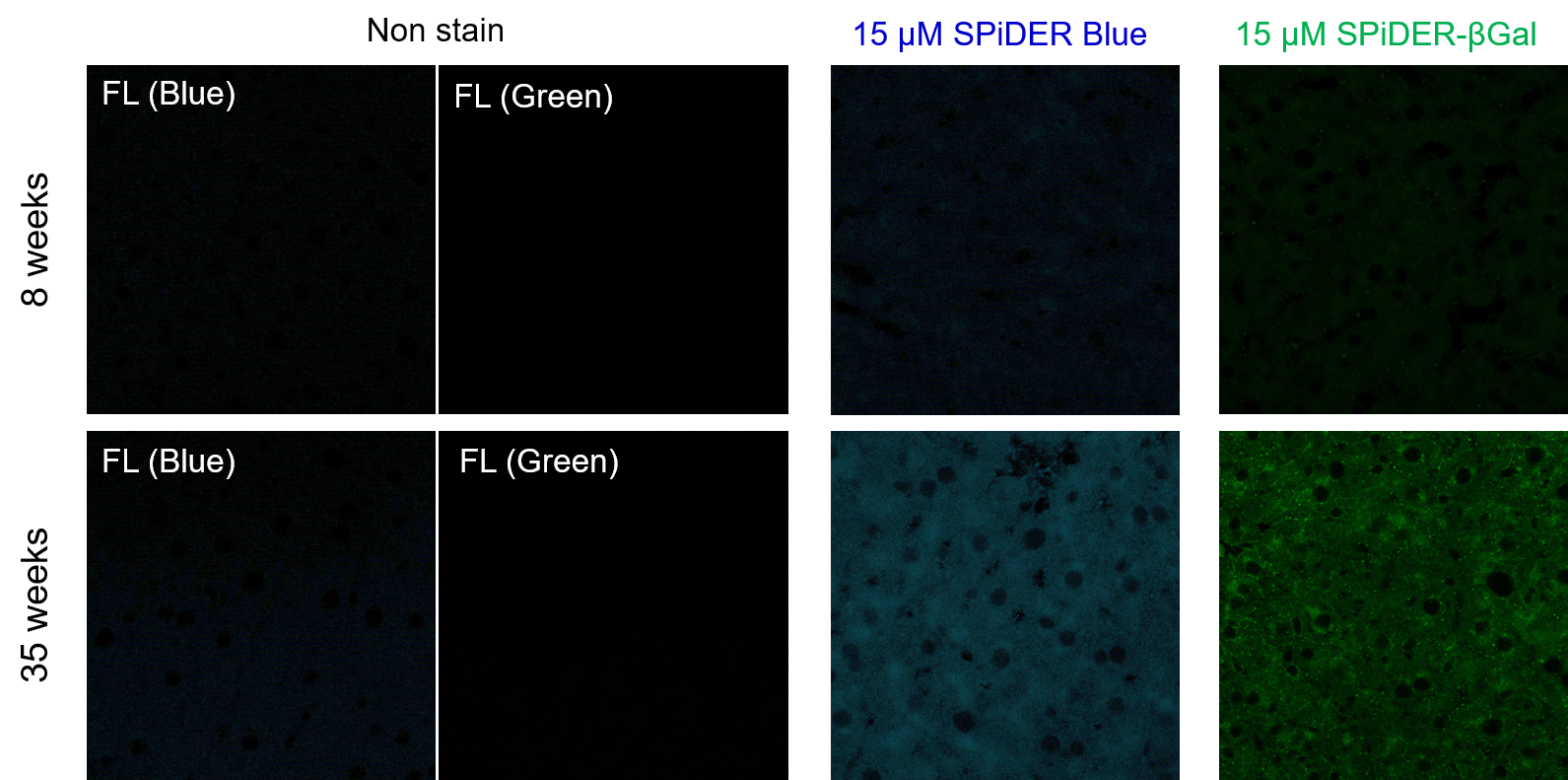
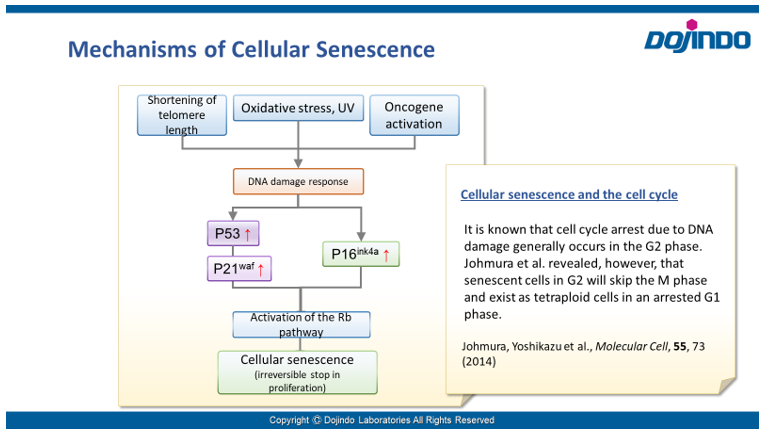
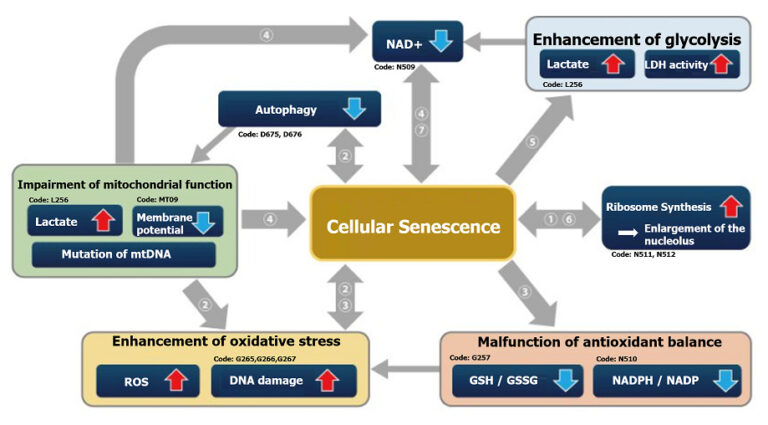
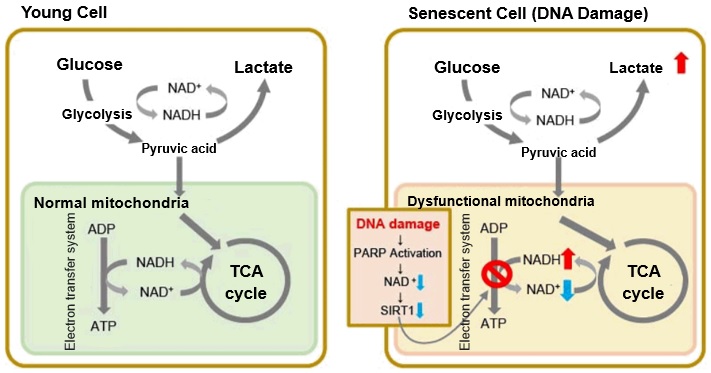
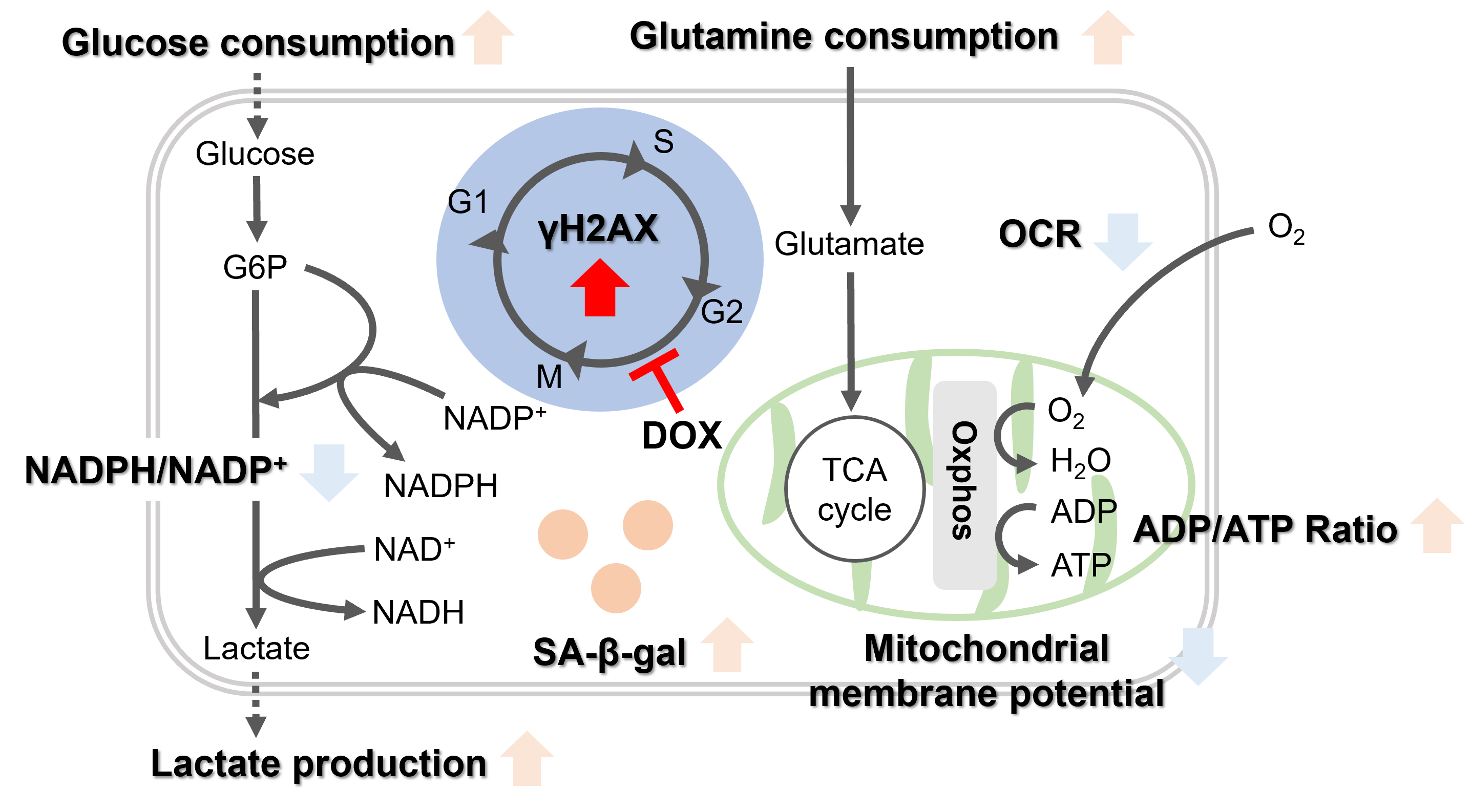
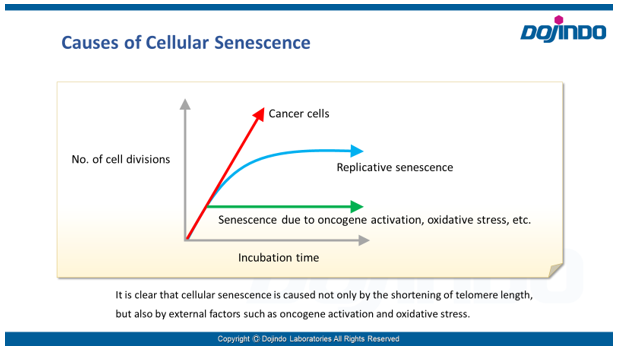 Senescence in cell biology refers to a state of permanent cell cycle arrest in response to stresses such as DNA damage or oncogene activation. Senescent cells can be identified by several molecular markers. Representative examples include p53, a transcription factor involved in the DNA damage response; p16, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that enforces cell cycle arrest; and senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-βgal). These cells resist apoptosis and ferroptosis and secrete inflammatory factors, collectively known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Although senescence plays protective roles such as tumor suppression in early stages, the accumulation of these cells over time promotes chronic inflammation and contributes to several age-related diseases. As immune-mediated clearance of senescent cells declines with age, understanding their biology is crucial for the development of therapies targeting ageing and its associated diseases.
Senescence in cell biology refers to a state of permanent cell cycle arrest in response to stresses such as DNA damage or oncogene activation. Senescent cells can be identified by several molecular markers. Representative examples include p53, a transcription factor involved in the DNA damage response; p16, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that enforces cell cycle arrest; and senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-βgal). These cells resist apoptosis and ferroptosis and secrete inflammatory factors, collectively known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Although senescence plays protective roles such as tumor suppression in early stages, the accumulation of these cells over time promotes chronic inflammation and contributes to several age-related diseases. As immune-mediated clearance of senescent cells declines with age, understanding their biology is crucial for the development of therapies targeting ageing and its associated diseases.