Lipi-Green

Lipid Droplet Staining
- High selectivity to lipid droplet (low background)
- 4 color available (blue, green, red, and deep red)
- High intracellular retentivity
- Applicable to both live and fixed cells
-
Product codeLD02 Lipi-Green
| Unit size | Price | Item Code |
|---|---|---|
| 10 nmol x 1 | $240.00 | LD02-10 |
Description
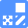
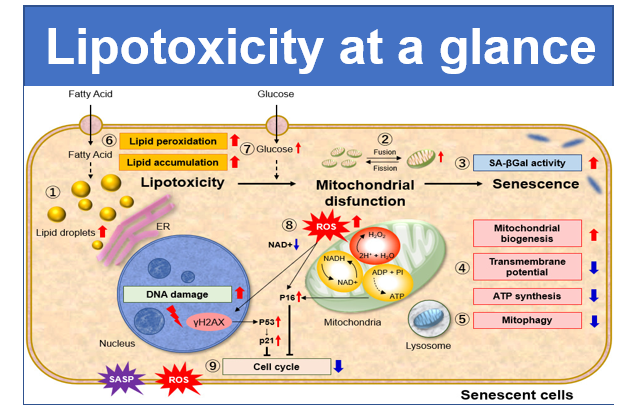
Lipid droplets (LDs) are composed of neutral lipids such as triacylglycerol & cholesteryl ester that are surrounded by phospholipid monolayers and are seen ubiquitously, not only in adipocytes1). LDs were originally thought to serve as a lipid storage unit, until a recent study showing that LDs play an important role in regulating lipid metabolism, autophagy2) and cellular senescence3). Therefore, LDs have gained great attention as an important tool to elucidate the mechanisms of their formation, growth, fusion, and retraction.
1) T. Fujimoto et al., “Lipid droplets: a classic organelle with new outfits.” Histochem Cell Biol., 2008, 130(2), 263.
2) R. Singh et al., “Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism.” Nature, 2009, 458(7242), 1131.
3) M. Yokoyama et al., “Inhibition of endothelial p53 improves metabolic abnormalities related to dietary obesity.” Cell Reports, 2014, 7(5), 1691.
For more information on Lipi-series and examples, please refer to the publication below:
4) Tatenaka, Y. et al., “Monitoring Lipid Droplet Dynamics in Living Cells by Using Fluorescent Probes” Biochemistry.“, 2019, 58(6), 499-503.
Notes: Lipi-Series is Patent Pending.
Manual
Technical info
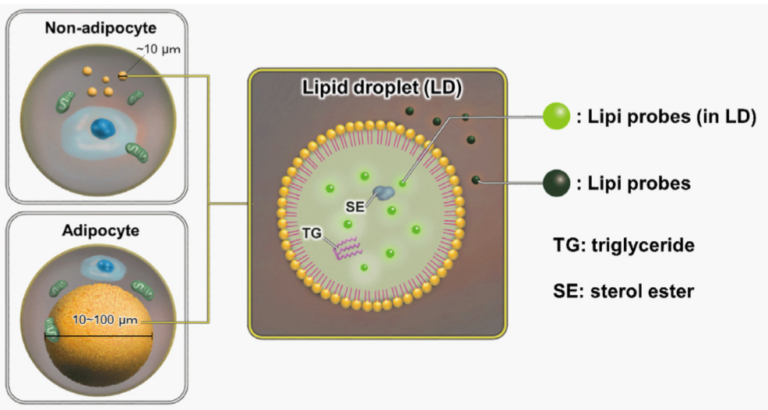
A medium that contained oleic acid (200 μmol/l) was added and incubated overnight. Then, the supernatant was removed and the cells were washed with PBS. Each Lipi product series (1 μmol/l) was added and the cells were incubated for 15 minutes.
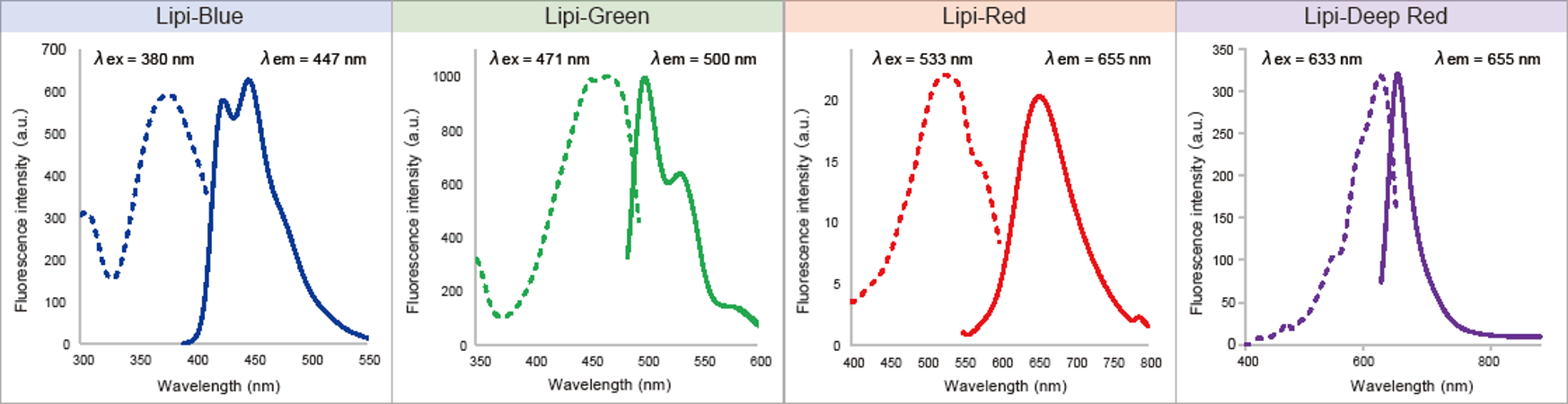
Lipi-Blue: Ex. 405 nm / Em. 450 – 500 nm
Lipi-Green: Ex. 488 nm / Em. 500 – 550 nm
Lipi-Red: Ex. 561 nm / Em. 565 – 650 nm
Lipi-Deep Red: Ex.640 nm / Em.650-700 nm
Reagent Comparison
The Lipi dyes have greatly improved the issues (specificity, color options, and retention) of existing lipid droplet staining reagents.
| Dojindo | Other Probes | ||||||
| Lipi-Blue | Lipi-Green | Lipi-Red | Lipi- Deep Red |
Oil Red O | Nile Red | Reagent B | |
| Live cells | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | ✓ |
| Fixed cells | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Specificity towards Lipid Droplets | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Higher Backgrounds than Lipi Dyes | ||
| Co-staining with Other Dyes*1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓*2 | ✓ | n.d. | -*3 | ✓ |
| Retention in Live Cells (24h) | ✓ | ✓ | - (1 h) | - (6 h) | n.d. | - |
- |
*1 For information on recommended filters with co-staining, please see the Q&A "Is there any information about filters used in co-staining?".
*2 A green fluorescence filter below 550 nm is recommended when co-staining with green fluorescence.
*3 Leaks in the GFP filter
High Intracellular Retentivity
Live HepG2 cells were stained with each of the Lipi products, Nile Red, and Reagent B.
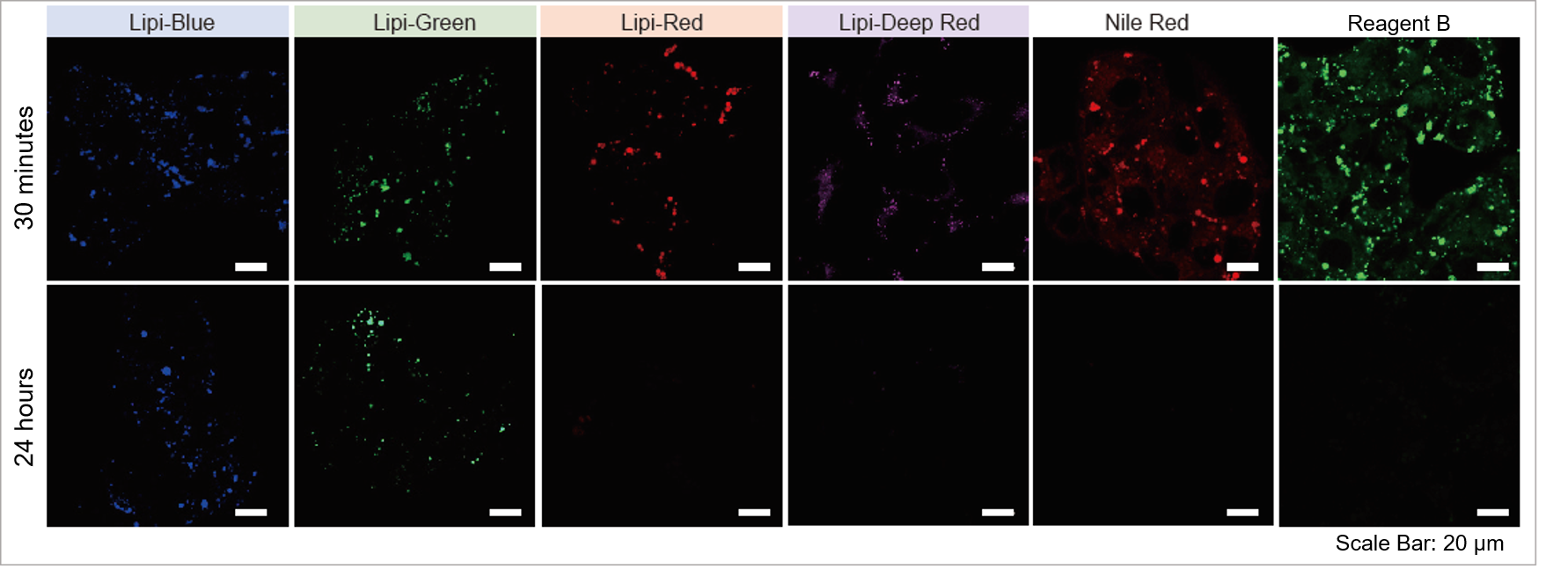
Lipi-Blue and Lipi-Green had higher retention in cells after 24 hours post staining than Lipi-Red, Nile Red, and Reagent B.
*For information on the retentivity time of Lipi-Red and Lipi-Deep Red, please refer to the Q&A 'How long will the Lipi-Series dyes be able to stain lipid droplets?'.
High Correlation with Antibody Detection Method: Lipi-Blue (LD01)
After fixing HepG2 with 4% PFA, cells are stained with 100 nmol/l Lipi-Blue. Then, Adipophilin (ADFP) expressed on lipid-droplet membrane was labeled with anti-ADFP antibody
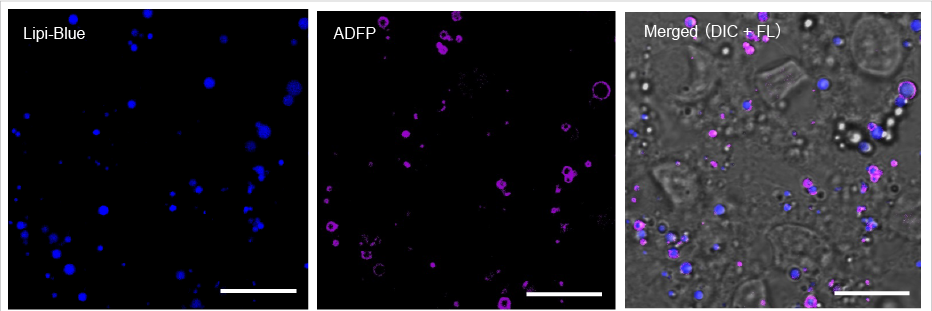
Scale Bar: 20 μm
Lipi-Blue: Ex. 405 nm / Em. 450 – 500 nm
Anti-ADFP antibody (Alexa Fluor® 647): Ex. 640 nm / Em. 650 – 700 nm
High Selectivity toward Lipid Droplet
Live HeLa cells were treated with Oleic acid and were stained with 100 nmol/l Lipi-Blue and 100 nmol/l Nile Red. Nile red had high background due to the limit in selectivity toward lipid droplets.
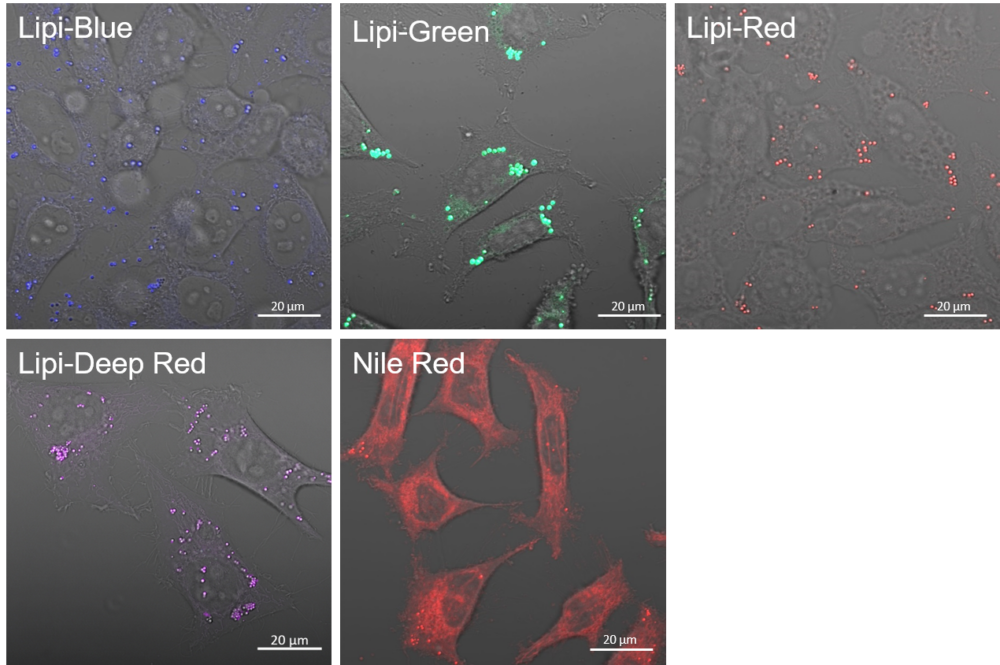
Lipi-Blue: Ex. 405 nm / Em. 450 -500 nm
Lipi-Green: Ex. 488 nm / Em. 500 – 550 nm
Lipi-Red: Ex. 561 nm / Em. 565 – 650 nm
Lipi-Deep Red: Ex. 640 / Em. 650 – 700 nm
Nile Red: Ex. 561 nm / Em. 565 – 650 nm
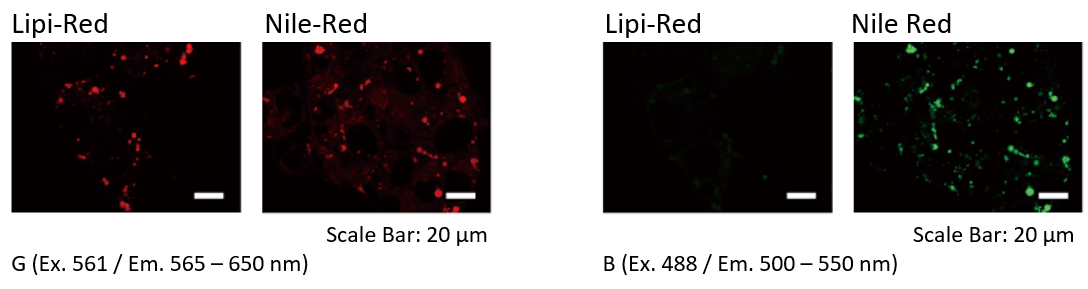
Filter Leakage Rate (Lipi-Red vs Nile Red)
HepG2 cells were stained with Lipi-Red and Nile Red. Lipi-Red was imaged with Green excitation (G), but not Blue excitation (B). However, Nile Red was imaged in both filter. Lipi-Red is preferable for multi-staining.
Experimental Example: Hepatotoxicity test of drug-induced lipidosis using high-content imaging
Propranolol (a sympathetic β-receptor blocker) was added to a human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HepG2 cells), and changes in lipid droplets were observed under a fluorescence microscope. The accumulation of lipid droplets was analyzed by measuring the number, area, and fluorescence intensity of lipid droplets from the acquired microscopic images.
Lipid droplet imaging
HepG2 cells were treated with propranolol 0, 10, or 30 μmol/l, lipid droplets were stained with Lipi-Green and nuclei with Hoechst 33342 and observed using a fluorescence microscope (Ti2-E inverted microscope). The results showed that lipid droplets increased in a propranolol concentration-dependent manner.
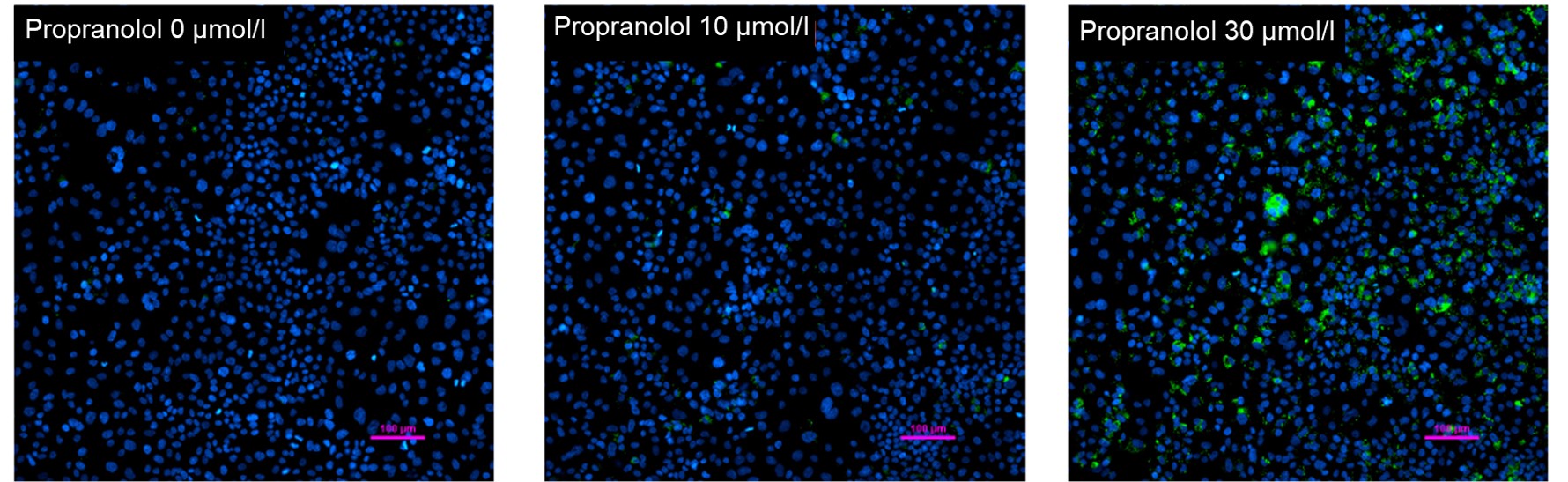
Nucleus (blue: Hoechst33342 ): Ex 385 nm, Em 460 nm
Fat droplet (green: Lipi-Green): Ex 475 nm, Em 535nm
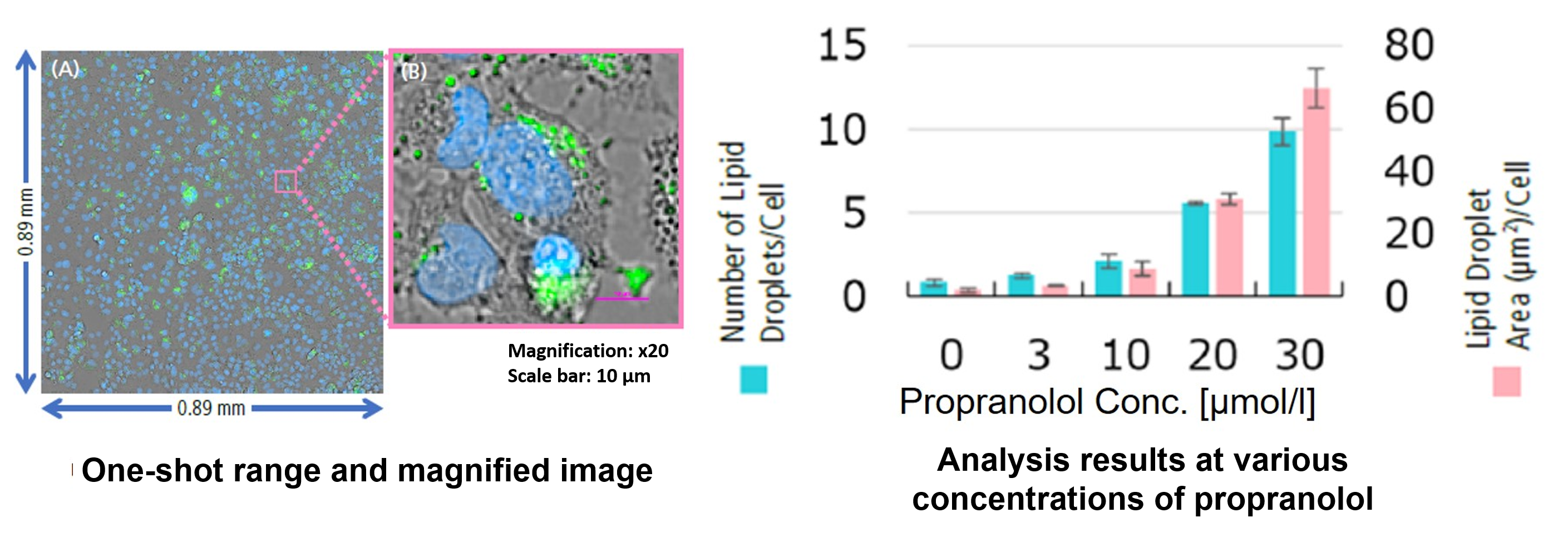
Analysis of fat droplet accumulation relative to drug treatment concentration
From the fluorescence images obtained, the accumulation of lipid droplets per cell was analyzed by measuring cell number from nuclei and area, number, and fluorescence intensity from lipid droplets. The results showed that the number and area of lipid droplets increased in a propranolol concentration-dependent manner, with lipid droplets forming significantly under concentration conditions of 20 μmol/l or higher. The DS-Qi2 camera, which can capture a wide range of cellular areas in a single shot, was used for imaging, and the EDF module of NIS-Elements software, which can acquire focused images of all lipid droplets, was used for analysis, enabling quantitative analysis with highly reliable statistical data. The EDF module of the NIS-Elements software allows for the acquisition of focused images of all lipid droplets.
<Equipment>
High Content Analysis (HCA) microscope system
(Nikon Corporation https://www.microscope.healthcare.nikon.com/)
For details of staining and analysis methods, please refer to "APPLICATION NOTE: Hepatotoxicity test of drug-induced lipidosis using high-content imaging" by Nikon Corporation.
Multiple Staining: Lipi-Deep Red (Purple) co-staining with GFP fluorescence (green) in HeLa cells
After adding Lipi-Deep Red (0.1 μmol/l) to the Arf4-GFP expressed Hela cells and the cells were incubated for 30 minutes, the cells were treated with 4% PFA (PBS) to fix, and washed with PBS three times. Fluorescent imaging was conducted by confocal microscopy.
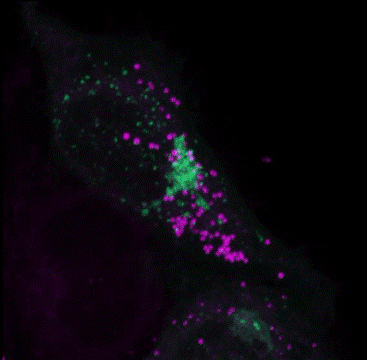
GFP: Ex/Em=488/400-552 nm
LDs: Ex/Em=640/630-700 nm
Multiple Staining: Lipi-Deep Red (RED) co-staining with GFP fluorescence (green) in HeLa cells
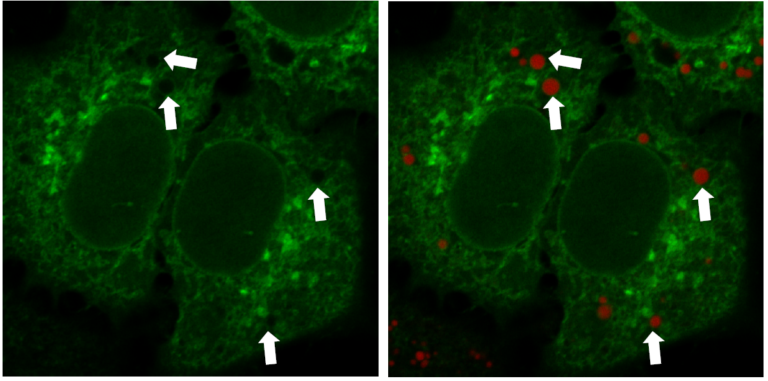
*Data was kindly provided by Dr. G. Belov, at University of Maryland, College Park
Multiple Staining: Reference
| No. | Sample | Multiple Staining | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1) | Brown Adipocytes | Co-stained with MitoBright Green (Mitochondria), Hoechst 33342 (Nuclear) and Lipi-Red | Masako, O. et al., “Exogenous Cytokine-Free Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Classical Brown Adipocytes”, Cells. 2019, 8(4), 373. |
| 2) | hMGEC | Co-stained with tandem RFP-GFP-tagged LC3B (autophagosome /autophagolysosome) and Lipi-Blue | Kim, S. et al., “Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) activates PPARγ signaling leading to cell cycle exit, lipid accumulation, and autophagy in human meibomian gland epithelial cells (hMGEC)“, The Ocular Surface, 2020, 18(3), 427-437. |
| 3) | AdMSCs | Co-stained with UCP1 antibody (Alexa Fluor 488), DAPI (Nuclear) and Lipi-Red | Yukimasa, T. et al.,” Transcriptome analysis reveals brown adipogenic reprogramming in chemical compound-induced brown adipocytes converted from human dermal fibroblasts”, Scientific Reports, 2021, 11, 5061. |
Adipocyte with Lipi Series
Lipid droplets in adipocyte were clearly detected by staining adipocytes, derived from 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, with Lipi-Series.
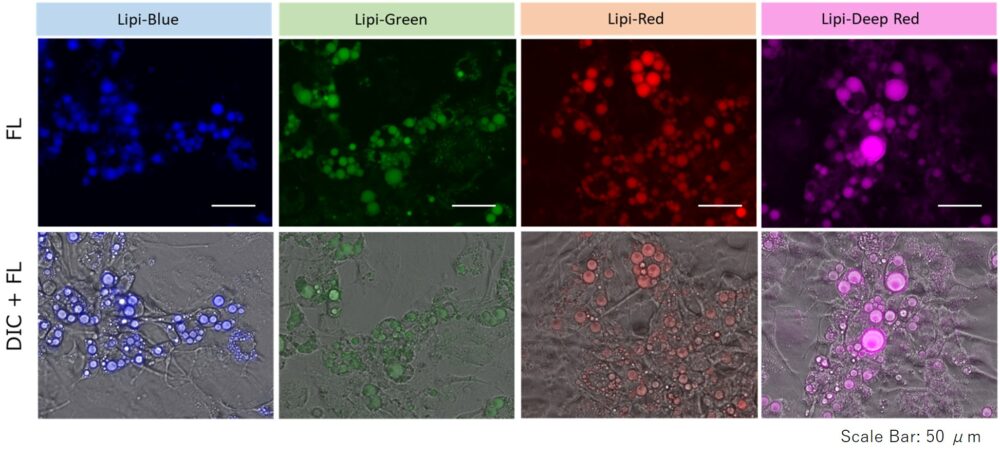
1. HeLa cells were seeded on a μ-slide 8-well plate and cultured at 37 ℃ overnight in a 5% CO2 incubator.
2. A conventional method was used to induce adipocyte differentiation.
3. The supernatant was removed and the cells were washed twice with DMEM (25 mmol/l glucose, 10% FBS, phenol red free).
5. The Lipi-series working solution (in DMEM (25 mmol/l glucose, 10% FBS, phenol red free)) was added and the cells were incubated at 37 ℃ for 24 hours in a 5% CO2 incubator.
6. The cells were observed using a fluorescence microscope.
*Dye Concentration: 2.5 µmol/L each.
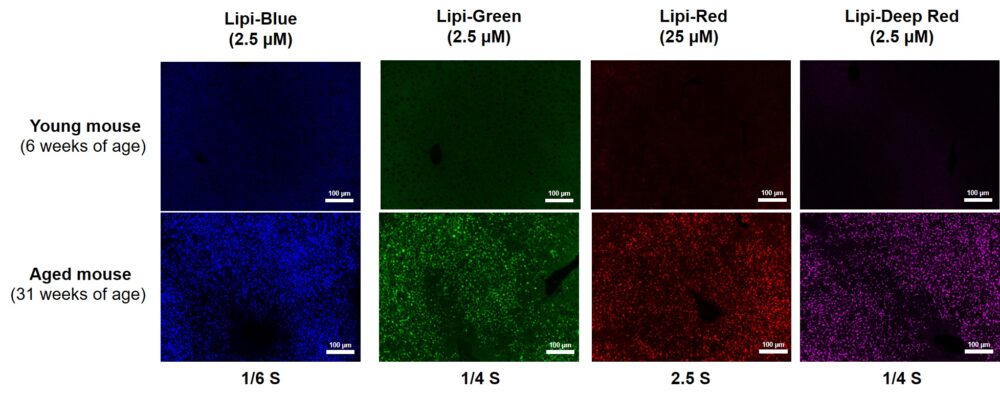
Mouse liver adipose tissue (Frozen section) with Lipi Series
After adding Lipi series to the 4% PFA (PBS) fixed mouse liver adipose tissue and the tissue were incubated for overnight, and washed with PBS. Fluorescent imaging was observed by fluorescence microscopy.
Positive control
Preparing a stock solution of oleic acid
Required Reagents:
・BSA (bovine serum albumin)
・Oleic acid
・0.1 mol/L Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)
Procedure:
(1) Dissolve 0.14 g/mL BSA in 0.1 mol/L Tris-HCl (pH 8.0).
(2) Add 4 mmol/L oleic acid to a disposable centrifuge tube.
(3) Add BSA solution (prepared in step 1).
(4) Cap the tube and mix on a rotary shaker (Be sure the solution is transparent, indicating that oleic acid has been conjugated to BSA).
(4) Filter the solution prepared above (step 4) using 0.22μm filter membranes.
(5) Store oleic acid stock solution at 4˚C.
*Use the appropriate amount of oleic acid stock solution for culture medium to prepare working solution. *Oleic acid working solution cannot be stored. Please prepare the working solution immediately before usage.
Inducing lipid droplets
(1) Incubate cells for 24 hours at 37˚C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere.
(2) Add 200 µmol/L working solution (prepared from oleic acid stock solution) to culture medium and incubate for further 24 hours.
Quantitative analysis
Changes in lipid droplets were examined after the addition of oleic acid or Triacsin C (acyl-CoA synthetase inhibitor) to the HepG2 cell culture medium. For analysis, the number and total area of lipid droplets per cell were computed from the images acquired with CQ1, a confocal quantitative image cytometer (Yokogawa Electric Corporation).
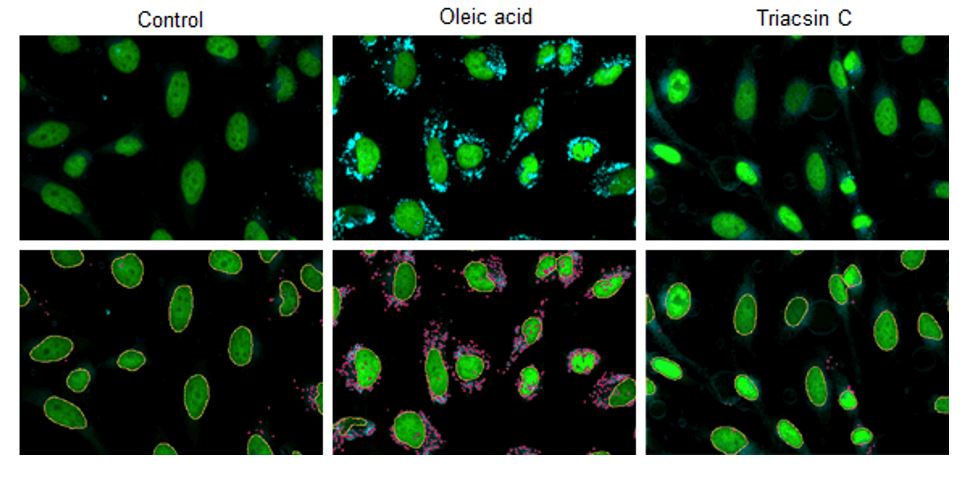
CQ1 captured images of lipid droplets with a 447/60 nm bandpass filter and cell nuclei with a 525/50 nm bandpass filter. Lipid droplets and cell nuclei were individually identified and computed the number and total area by using the CellPathfinder analysis software.
Imaging conditions:
Plate: 96 well plate, objective lens: x 20
excitation: 405 nm (Lipi-Blue), blue/488 nm (SYBR Green), Green
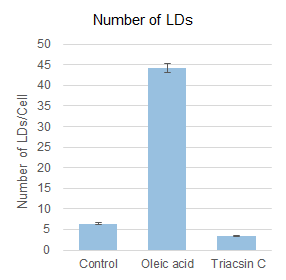
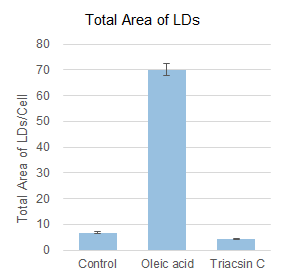
Based on the detected data of cell nuclei and lipid droplets, the number and total area of lipid droplets per cell computed were shown in the graphs below. Compared to the control value, the number and total area of lipid droplets per cell were increased 7-10 times by the addition of oleic acid, but the addition of Triacsin C inhibited lipid droplet formation and showed a 50-60% decrease.
Experimental conditions
HepG2 cells (1 x 103 cells) were disseminated on a 96-well plate and incubated overnight. After the culture supernatant was removed, the cells treated with DMEM plus FBS only (control), DMEM plus FBS and 200 μmol/L oleic acid (Oleic acid), and DMEM plus FBS and 5 μmol/L Triacsin C (Triacsin C) were incubated overnight. Cells were then washed twice with PBS buffer, fixed with 4% PFA for 5 minutes at room temperature, and washed twice with PBS buffer again. Finally, cells were stained in the dark for 2 hours at room temperature with 0.5 μmol/L Lipi-Blue working solution, and quantitative analysis was performed through CQ1.
Related Product Information
| Function | Product | Size | Product Code |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Imaging |
Lipi-Blue | 10 nmol | LD01 |
| Lipi-Green | 10 nmol | LD02 | |
| Lipi-Red | 100 nmol | LD03 | |
| Lipi-Deep Red | 10 nmol | LD04 | |
|
Quantification (Plate Reader, FCM) |
Lipid Droplet Assay Kit - Blue | 1 set | LD05 |
| Lipid Droplet Assay Kit - Deep Red | 1 set | LD06 |
Recommended Filter: Wavelength for Excitation and Emission
References
1) Y. Tatenaka, H. Kato, M. Ishiyama, K. Sasamoto, M. Shiga, H. Nishitoh and Y. Ueno, "Monitoring Lipid Droplet Dynamics in Living Cells by Using Fluorescent Probes", Biochemistry., 2019, DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01071 .
Q & A
-
Q
Which filters are recommended for co-staining?
-
A
Select filters suitable for co-staining according to the dyes and excitation wavelengths you use. Refer to the table below for recommended filter ranges.
Excitation wavelength
405 nm
(Hoechst, DAPI etc.)488 nm
(FITC, GFP etc.)561 nm
(Cy3, Rhodamine, RFP etc.)633 nm
(Cy5, mCherry etc.)Lipi-Blue
Lipi-Blue detection
Lipi-Blue is not excited at 488, 561, or 633 nm, so it can be used with any fluorescence filter.
Lipi-Green
Lipi-Green shows slight excitation at 405 nm. Fluorescence filters within the 400–500 nm range are recommended to minimize spectral overlap.
Lipi-Green detection
Lipi-Green is not excited at 561 or 633 nm. Thus, these channels can be used without interference from Lipi-Green.
Lipi-Red
Lipi-Red shows slight excitation at 405 nm. Fluorescence filters within the 400–500 nm range are recommended to minimize spectral overlap.
Lipi-Red shows slight excitation at 488 nm. Fluorescence filters within the 500–550 nm range are recommended to minimize spectral overlap.
Lipi-Red detection
Lipi-Red shows slight excitation at 633 nm. Fluorescence filters within the 650–700 nm range are recommended to minimize spectral overlap.
Lipi-Deep Red
Lipi-Deep Red is not excited at 405 or 488 nm. Thus, these channels can be used without interference from Lipi-Deep Red.
Lipi-Deep Red shows slight excitation at 561 nm. Fluorescence filters within the 560–610 nm range are recommended to minimize spectral overlap.
Lipi-Deep Red detection
-
Q
What should I do if the fluorescence is not detected?
-
A
1. Filter conditions
Check the fluorescence spectrum of the dye on the product HP and confirm if the excitation / emission wavelength for your filter is suitable.
2. Concentration of Lipi probe working solution
Optimize the concentration within the following range:
Lipi-Blue, Lipi-Green: 0.1-0.5 μmol / L
Lipi-Red: 1-5 μmol / L
* If fluorescence is not detected even under the above conditions, prepare a higher concentration of the working solution.
Lipi-Blue & Lipi-Green: 1-2 μmol / L
Lipi-Red: 10 – 20 μmol / L3. Incubation time
Incubate for 1-2 hours after adding Lipi probe working solution.4. Assay conditions (fixed cells)
Please refer to Q2.5. Other
Depending on the cell type, lipid droplets can be smaller than usual and it may be too difficult to observe.
If that is the case, please observe under a high magnification microscope or prepare for positive control with oleic acid treated cells.
-
Q
Can I use Lipi-dye for fixed cells?
-
A
Yes, Lipi-dye can be used for fixed cells.
* Please use paraformaldehyde (PFA) for fixation. Methanol fixation is not recommended because it may affect the staining of lipid droplets.
* Depending on the cell, the sequence of staining and fixation may affect the staining results. If it does not stain or the sensitivity is weakened, please consider the sequence of staining and fixation to improve the staining results.
-
Q
Can I use Lipi-dye for frozen tissue?
-
A
Yes, Lipi-dye can be used for frozen tissue.
* Please use paraformaldehyde (PFA) for fixation. Alcohol fixation is not recommended because it may affect the structure of lipid droplets.
○ Mouse liver adipose tissue <Frozen section>
1. Add 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA)/PBS solution to the mouse liver adipose tissue (Frozen section) and incubate at room temperature for 5 minutes.
2. Remove the supernatant and wash with PBS, and add the Lipi-series Working solution (in PBS) in the cells and incubated at 4 ℃ for overnight.
3. Remove the supernatant and wash with PBS, observe under a fluorescence microscope.
-
Q
How long will the Lipi-Series dyes be able to stain lipid droplets?
-
A
We have confirmed the retentivity (no loss of fluorescence signal) of Lipi-Green and Lipi-Blue up to 24 hours, Lipi-Red up to 1 hour, and Lipi-Deep Red up to 6 hours.
We have confirmed the dye retention by the following steps.1. The medium of overnight cultured HepG2 cells was removed and the cells were washed twice with DMEM medium FBS(-).
2. The supernatant was removed and the working solution prepared in DMEM medium FBS(-) was added.
・Lipi-Blue: 0.1 µM
・Lipi-Green: 0.1 µM
・Lipi-Red: 1 µM
・Lipi-Deep Red: 0.1 µM
3. Incubated for 30 min (5% CO2, 37 °C).
4. The medium was replaced with DMEM medium FBS(+).
5. Observed by fluorescence microscopy after 30 minutes, 1, 3, 6 hours, and 24 hours.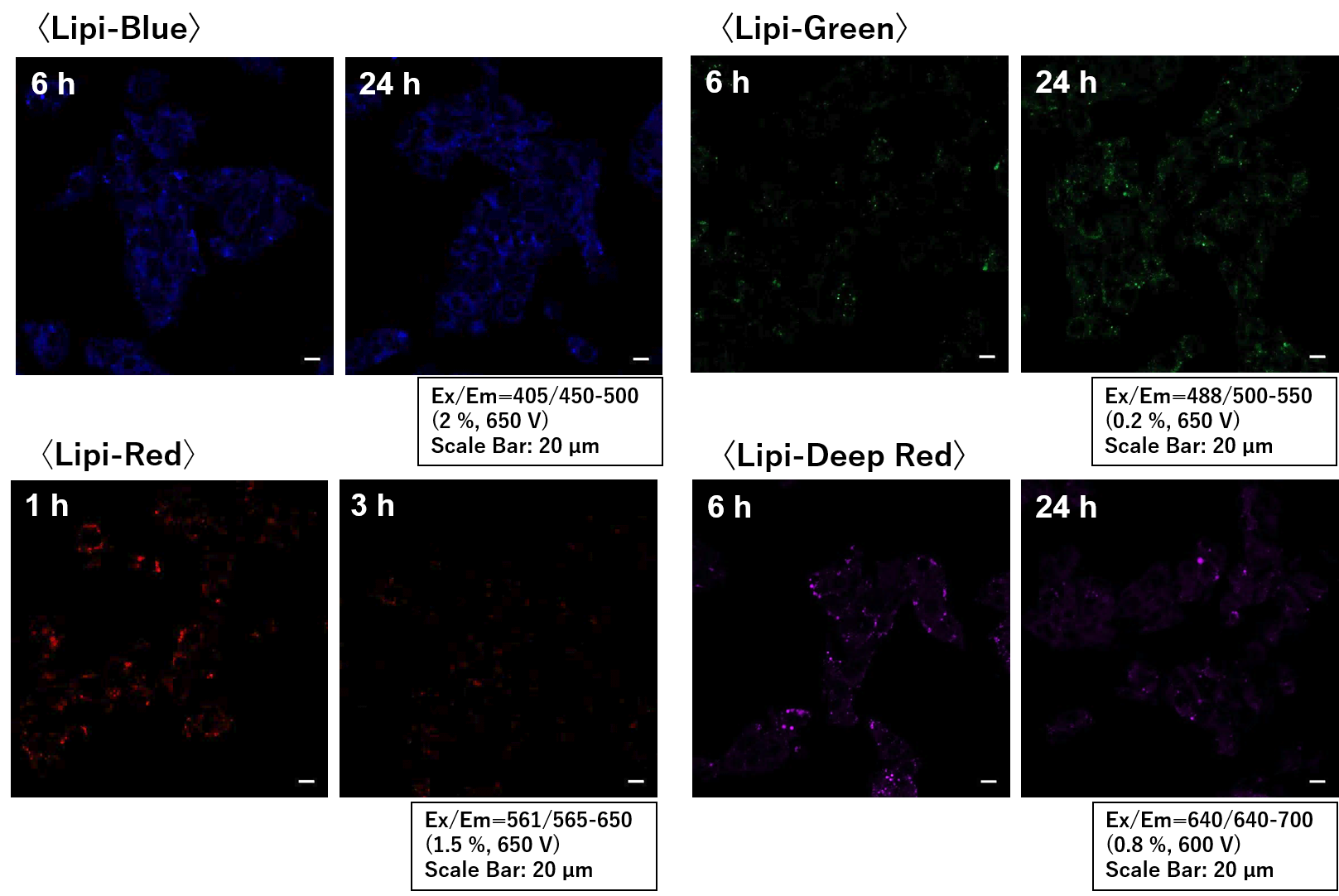
-
Q
Are there any important tips for tissue staining?
-
A
When staining tissue, it takes time for the dyes to penetrate the tissue, so a long staining time (24 hours or more) is required to obtain a lipid droplet stained image.
We have seen better results by treating the tissue with a 60% isopropanol solution for 2 minutes before staining with Lipi dye for 30 minutes.〇 Used Mice
STAM* mice (8 weeks old)
*STAM™ model: Pathological progression similar to human MASH/NASH-HCC and accumulation of lipid droplets.
〇 Protocol1. Tissue was air dried at room temperature for 30 min.
2. Tissue was treated with 4 % PFA/PBS (RT, 10 min) and washed twice with PBS.
3. 60 % isopropanol treatment (RT, 2 min), and washed twice with PBS.
4. Lipi-dye (DMSO stock solution) was diluted 40-fold with PBS and then added.
5. Incubated at room temperature for 30 min.
6. Tissue was washed twice with PBS.
7. Embedded in Prolong Antifade and observed after slice thinning.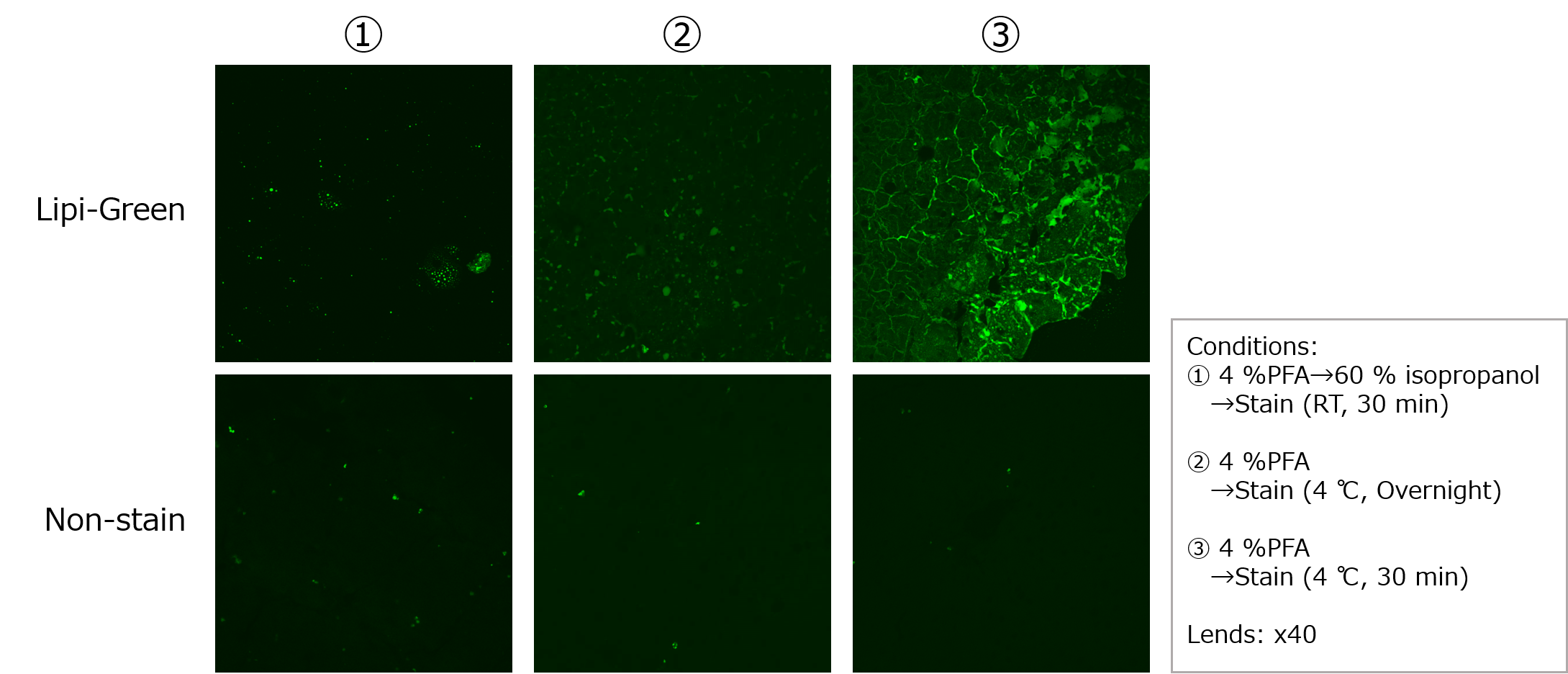
-
Q
Can Lipi-Green be used with a flow cytometer?
-
A
Lipi-Green is not suitable for flow cytometry. However, Lipi-Blue and Lipi-Deep Red can be used for fluorescence measurement with a flow cytometer. For flow cytometer analysis, the following assay kits are available.
Product name Product code Lipid Droplet Assay Kit - Blue LD05 Lipid Droplet Assay Kit - Deep Red LD06
Handling and storage condition
| Appearance: | Yellowish orange to orange solid |
|---|---|
| Purity (HPLC): | ≧ 85.0 % |
| Ambient temperature |